Key Takeaways
- Thymagen (Thymogen) is not FDA-approved and is available for research purposes only.
- Typical dosing protocols are derived from preclinical studies, focusing on T-cell differentiation and nucleic acid synthesis.
- Titration schedules are essential for optimizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- Thymagen (Thymogen) is administered as a lyophilized powder, typically reconstituted for subcutaneous injection.
- Medical supervision is crucial to adjust dosing based on individual factors like body weight and treatment goals.
What Is Thymagen (Thymogen)?
Thymagen (Thymogen) is a synthetic dipeptide derived from thymic extracts, primarily used in research settings to study T-cell differentiation and nucleic acid synthesis. It functions by modulating thymic receptor signaling pathways. For more detailed information, visit our Thymagen (Thymogen) profile.
Standard Dosing Protocols
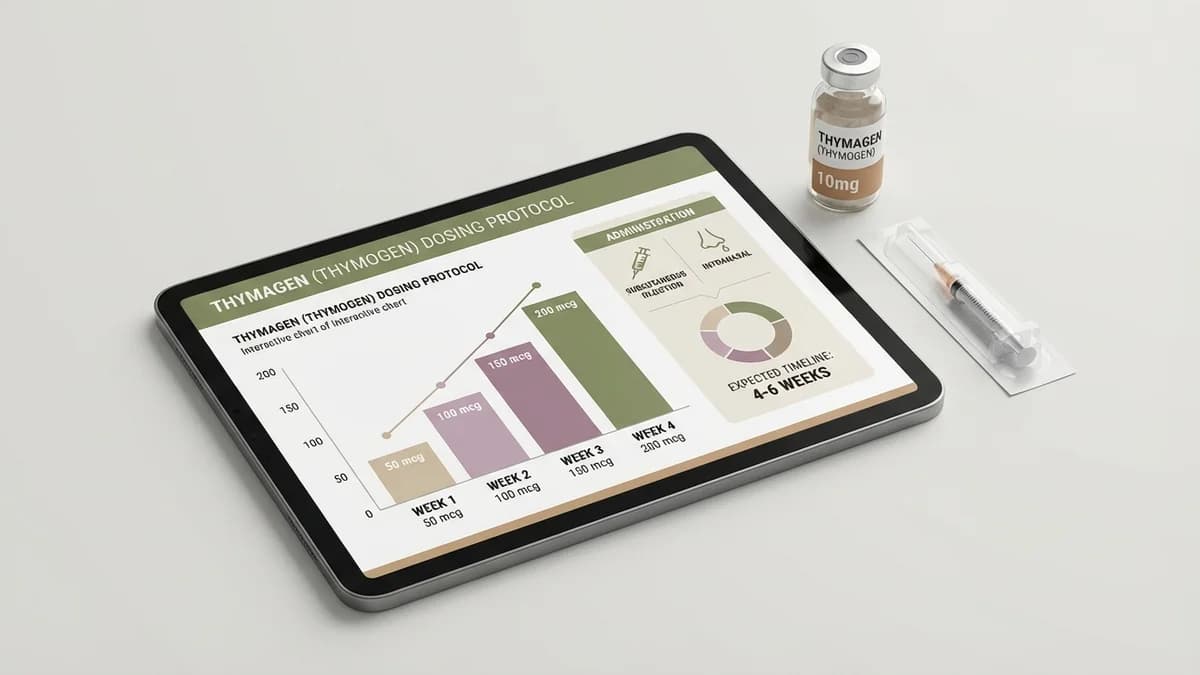
Thymagen (Thymogen) is not FDA-approved for any therapeutic use, and thus, there are no standardized dosing protocols sanctioned by regulatory bodies. The dosing information available comes from preclinical studies and research protocols. For instance, studies have used varying concentrations to assess its effects on T-cell differentiation (PMID 1659006). Researchers typically tailor dosing based on study design and specific research objectives.
Titration Schedules
Titration is a critical component of Thymagen (Thymogen) administration, as it helps balance efficacy and tolerability. In research settings, doses may start at a lower concentration and gradually increase based on observed responses and side effect profiles. This approach helps in understanding the peptide's pharmacodynamics and optimizing its effects on the immune system.
Administration Method
Thymagen (Thymogen) is provided as a lyophilized powder intended for research use. It is commonly reconstituted with sterile water and administered via subcutaneous injection. Proper injection site rotation is recommended to minimize local irritation. Needles typically used are 27-30 gauge, and storage of the reconstituted solution should follow specific guidelines to maintain stability and efficacy.
Factors That Affect Dosing
Several factors influence Thymagen (Thymogen) dosing, including:
- Body Weight: Heavier individuals may require adjusted dosing to achieve the desired therapeutic effects.
- Treatment Goals: Specific research objectives, such as enhancing T-cell differentiation or nucleic acid synthesis, may dictate dosing variations.
- Concurrent Medications: Interactions with other substances can influence Thymagen's efficacy and safety profile.
- Organ Function: Liver and kidney function can affect peptide metabolism and clearance, necessitating dose adjustments.
What Happens If You Miss a Dose
In a research setting, missing a dose of Thymagen (Thymogen) should be addressed by consulting the study protocol or a supervising researcher. Generally, it is advised not to double up on doses but to continue with the regular schedule.
Dosing Compared to Similar Peptides
Thymagen (Thymogen) shares functional similarities with other thymic peptides like thymosin alpha-1, which is used in some clinical settings for immune modulation. However, unlike thymosin alpha-1, Thymagen is primarily limited to research applications and lacks standardized clinical dosing guidelines.
What the Evidence Does Not Show
Current research on Thymagen (Thymogen) is primarily preclinical, with limited human data available. Long-term safety and efficacy in therapeutic contexts remain largely unexplored. Future studies are needed to establish comprehensive dosing guidelines and validate its potential clinical applications.
FAQ
1. Is Thymagen (Thymogen) safe for human use? Thymagen (Thymogen) is not approved for human use and is available for research purposes only. Safety in humans has not been established.
2. How is Thymagen (Thymogen) administered? It is typically reconstituted as a solution for subcutaneous injection, following specific research protocols.
3. Can Thymagen (Thymogen) be used concurrently with other peptides? Concurrent use with other peptides should be approached with caution and under research supervision due to potential interactions.
4. What should I do if I experience side effects during a study? Report any side effects to the supervising researcher or clinician immediately for assessment and management.
5. How does Thymagen (Thymogen) compare to thymosin alpha-1? While both are thymic peptides, Thymagen is primarily used in research, whereas thymosin alpha-1 has some clinical applications for immune modulation.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider before starting any treatment.
Find a Peptide Therapy Clinic Near You
Browse our directory of verified peptide therapy clinics across the United States. Compare providers, read reviews, and request a consultation.
PeptideClinicLocator.com does not provide medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any peptide therapy. Regulatory status may change.